
In the episode of our LocalGov Drupal series of tutorials, we are presenting an alternative way to set up your first LocalGov Drupal website locally, using DDEV.
This is the second episode in our LocalGov Drupal series of tutorials:
LocalGov Drupal: Multiple local development methodologies supported
In this second tutorial of our LocalGov Drupal series, we are going to use DDEV to set up our first LGD website locally. In our first tutorial, we did the same using Lando instead but both ways are valid and it's just a matter of preference which technology to use.
Requirements
Similarly to our previous tutorial using Lando, we need a few things in place first (in this order):
- Composer
- Docker Desktop
LandoDDEV
We have already covered the first two requirements so we'll only need to expand on ddev in this post.
DDEV

DDEV is an open-source tool for launching local web development environments in minutes. It supports PHP, Node.js, and Python. These environments can be extended, version controlled, and shared, so you can take advantage of a Docker workflow without Docker experience or bespoke configuration. Projects can be changed, powered down, or removed as easily as they’re started.
DDEV has its own requirements, also dependent on the Operating System you're using. The corresponding page on the DDEV documentation offers detailed information on the prerequisites that should be in place but, generally speaking, here's a list of minimum requirements for DDEV:
- Recent OS version
- RAM: 8 GB
- Storage: 256GB
Installing DDEV
There are multiple ways of installing DDEV locally, mainly depending on your Operating System. Make sure you go through the official documentation on DDEV installation if your OS is not covered below:
1. DDEV on Mac OS
DDEV using Homebrew:
Homebrew is a popular package manager for Mac OS and Linux - it basically brings packages into your machine in an organised manner. It controls and manages their dependencies and versions (similar to Composer). To install Homebrew locally:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"With Homebrew in place, run the following to install DDEV:
brew install ddev/ddev/ddevYou can confirm that DDEV is in place by checking its installed version:
ddev -vDDEV using curl:
To download and run the install script, run the following in your Terminal:
curl -fsSL https://ddev.com/install.sh | bash2. DDEV on Windows
You can install DDEV on Windows in three ways:
- Using WSL2 with Docker inside
- Using WSL2 with Docker Desktop
- Installing directly on traditional Windows with an installer
DDEV strongly recommends using WSL2. While its Linux experience may be new for some Windows users, it’s worth the performance benefit and common experience of working with Ubuntu and Bash. You can follow the official documentation's steps to install DDEV using WSL2 with Docker Desktop.
3. DDEV on Linux
You can use Homebrew or the curl install script in most instances, as described in the Mac OS installation instructions. On the DDEV documentation pages, there are more installation ways listed for some Linux and Ubuntu distributions.
Local Installation steps
Now that we have Composer, Docker Desktop and DDEV installed on our local machine, we can proceed with setting up our first LocalGov Drupal project locally.
Open your Command Prompt/Terminal and switch to an appropriate directory (for example, on Mac OS X, the ~/Sites folder is usually preferred):
cd ~/Sites1. Creating the project
Similarly to our Lando installation guide, we are going to use the LGD project template publicly available on GitHub, https://github.com/localgovdrupal/localgov_project:
composer create-project localgovdrupal/localgov-project LGD_DEMO --no-install The output should look something like the following:
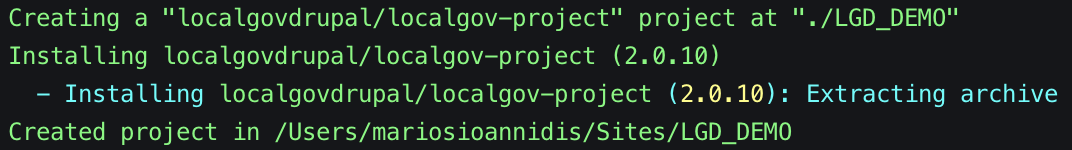
Switch to the LGD_DEMO directory by running:
cd LGD_DEMO2. The DDEV part
Then, we need to initialise our DDEV project:
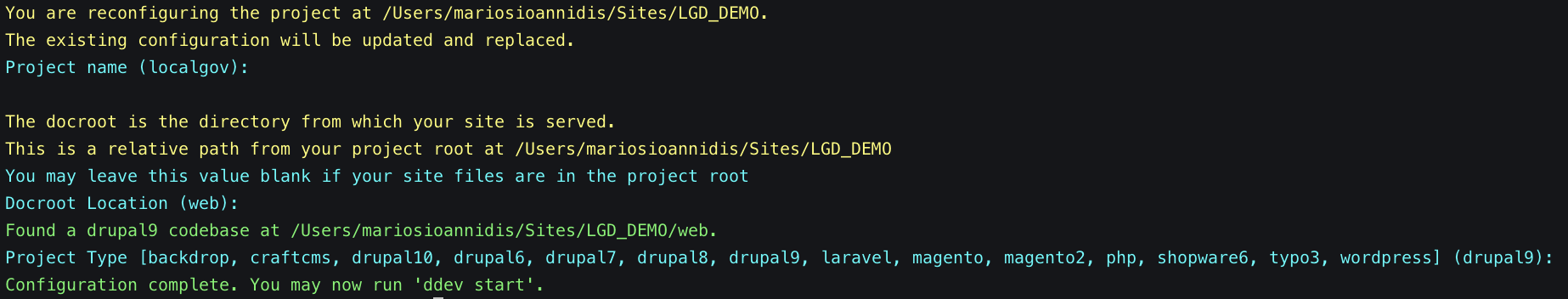
ddev configAs you can see in the screenshot below, DDEV is suggesting default values for the following:
- Project name (suggested default: locagov)
- Docroot location (suggested default: web)
- Project Type (suggested default: drupal9)
We complete the initialisation by hitting "Enter" in all three suggestions so the default value is selected. The output of the command should look like the following:
Then, fire up DDEV:
ddev startInitially, the required resources are pulled in:
Following that, the containers start running:
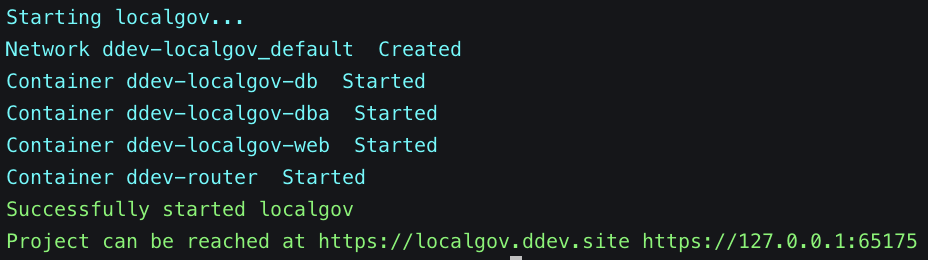
Every time ddev starts, the project URLs are included in the output. In our case, we have selected "localgov" as the name of our project and, as a result, https://localgov.ddev.site will be the first URL we can access our project on. The second URL, https://127.0.0.1:65175, uses our machine's localhost IP and an available port allocated to our ddev project. Both URLs can be used to access our project on our browser.
Once DDEV has been initialised, you might also want to run:
ddev auth sshin order to enable your SSH keys for this project (this is useful for SSH authentication in case access to remote repositories is required). The output of this command lists all the SSH keys our container has been made aware of.
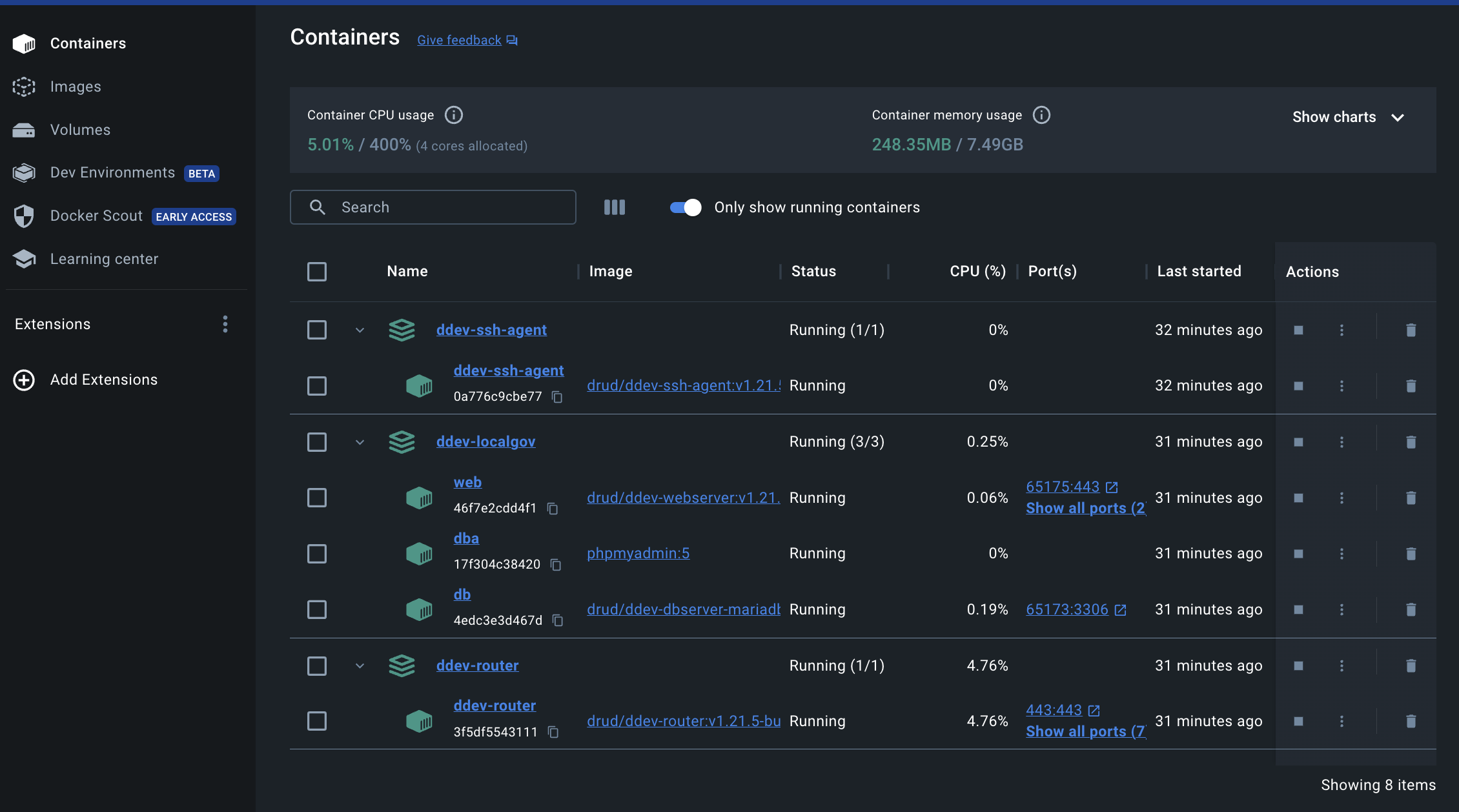
The Docker dashboard, with all our LGD demo project's DDEV containers up and running, should look something like the following:
3. The composer install part
Now it's time to pull in all the Composer dependencies for this project:
ddev composer installIf it's the first time running composer install, this process can take a while because all the project's dependencies need to be brought in from their repositories. We have already covered the various stages of this Composer command's output in our LGD Lando tutorial. Upon re-running the same command, the Terminal should naturally inform us that there is Nothing to install, update or remove.
4. Building the site with drush
We can now finally install our site using the site install drush command (for more on drush, Drupal's popular scripting tool, see https://www.drush.org):
ddev drush si localgov -yThe output of the command will look something like the following:
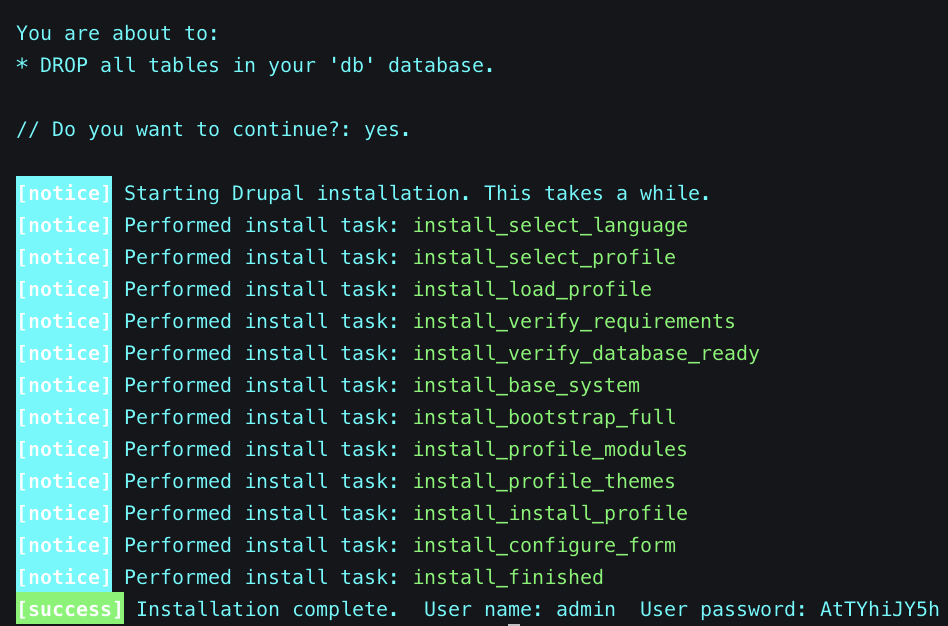
Our new LocalGov Drupal site is now up and running locally! Remember those two project URLs returned by ddev start above? You can use either one of them, and the credentials returned from the last command, to access your Drupal administrator account on your brand new LGD site on your favourite browser:
Logging into your admin account will land you on the Drupal content page:
Conclusion
Your brand new LocalGov Drupal site is now up and running locally with DDEV. From here, you can explore all the unique features that come with LGD out of the box and start building your new Council website!
Let us know what you think of our LocalGov Drupal tutorial, we greatly appreciate any feedback.
ORION WEB can help your Council design and build its brand-new Local Government website or microsite, as well as migrate your legacy site to the LGD platform. Contact us for a free demo of LGD's features - we'd love to discuss your Council's digital strategy!
